There are many types of transmission. Among the four types of transmission methods (mechanical, electrical, hydraulic and pneumatic) that are widely used at present, none of the power transmissions is perfect. Today, I will share with you the advantages and disadvantages of the four transmission methods.
1. Mechanical transmission
A. Gear drive
Gear transmission is the most widely used transmission form in mechanical transmission. It has relatively accurate transmission, high efficiency, compact structure, reliable operation and long service life. Gear transmission can be divided into many different types according to different standards.
Advantage:
Compact structure, suitable for short-distance transmission; suitable for a wide range of peripheral speed and power; accurate, stable, and high-efficiency transmission ratio; High reliability and long service life; It can realize the transmission between parallel axis, arbitrary Angle intersecting axis and arbitrary Angle staggered axis.
Shortcoming:
It requires high manufacturing and installation accuracy and high cost; it is not suitable for long-distance transmission between two shafts; there is no overload protection.
B. Turbine shaft transmission
It is suitable for motion and dynamics between two axes that are perpendicular but not intersecting in space.
The main parameters of the turbine shaft transmission are: modulus; pressure angle; turbine index circle; lead; number of turbine teeth; number of turbine heads; transmission ratio, etc.
Advantages: large transmission ratio; compact structure and size.
Disadvantages: large axial force, easy to heat, low efficiency, only one-way transmission.
C. Belt drive
A belt drive is a mechanical transmission that uses a flexible belt tensioned on a pulley for motion or power transmission. The belt drive usually consists of a driving pulley, a driven pulley and an endless belt tensioned on the two pulleys.
1) It is used for the occasions where the two axes are parallel to the same rotation direction, which is called the concept of opening movement, center distance and wrapping angle.
2) The type of belt can be divided into three categories: flat belt, V belt and special belt according to the cross-sectional shape.
3) The key points of application are: calculation of transmission ratio; analysis and calculation of belt stress; allowable power of a single V-belt.
4) Main features of belt drive:
Advantage:
It is suitable for transmission with large center distance between two shafts. The belt has good flexibility, which can ease the impact and absorb vibration; it slips when overloaded to prevent damage to other parts; the structure is simple and the cost is low.
Shortcoming:
The outer dimension of the transmission is large; a tensioning device is required; due to slippage, a fixed transmission ratio cannot be guaranteed; the life of the belt is short; the transmission efficiency is low.
D. Chain drive
Chain drive is a transmission method that transmits the motion and power of the driving sprocket with special tooth shape to the driven sprocket with special tooth shape through the chain. Including active chain, driven chain, endless chain.
Advantages: The chain drive has many advantages. Compared with the belt drive, there is no elastic sliding and slipping phenomenon, the average transmission ratio is accurate, the work is reliable, and the efficiency is high; the transmission power is large, the overload capacity is strong, and the transmission size under the same working conditions is small; all The tension force is small, and the pressure acting on the shaft is small; it can work in harsh environments such as high temperature, humidity, dust and pollution.
Compared with gear transmission, chain transmission requires lower manufacturing and installation accuracy; when the center distance is large, its transmission structure is simple; the instantaneous chain speed and instantaneous transmission ratio are not constant, and the transmission stability is poor.
Disadvantages: The main disadvantages of chain drive are: it can only be used for transmission between two parallel shafts; high cost, easy to wear, easy to elongate, poor transmission stability, additional dynamic load, vibration, shock and noise during operation, not suitable for use in a sharp reverse drive.
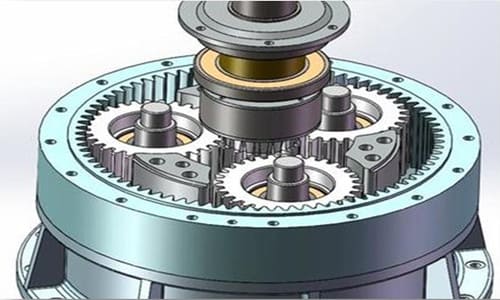
E. Geartrain
A transmission consisting of more than two gears is called a gear train. Gear transmission can be divided into ordinary gear transmission and planetary gear transmission according to whether there are gears with axial movement in the gear train. The gears with axial movement in the gear train are called planetary gears.
1) The gear train is divided into two types: fixed axle gear train and epicyclic gear train.
2) The ratio of the angular velocity (or rotational speed) of the input shaft to the output shaft in the gear train is called the gear ratio of the gear train. It is equal to the ratio of the product of the number of teeth of all driven gears and the number of teeth of all driving gears in each pair of meshing gears.
3) In the epicyclic gear train, the gear whose axis position changes, that is, the gear that both rotates and revolves, is called the planetary gear, and the gear whose axis position is fixed is called the center gear or the sun gear.
4) The transmission ratio of the epicyclic gear train cannot be calculated directly by the method of solving the transmission ratio of the fixed shaft gear train. The principle of relative motion must be used to convert the epicyclic gear train into an imaginary The fixed axle gear train is calculated.
5) The main features of the gear train:
It is suitable for transmission between two shafts that are far apart; it can be used as a transmission to realize variable speed transmission; a larger transmission ratio can be obtained; it can realize the synthesis and decomposition of motion.
2. Electric drive
Electric drive refers to the use of electric motors to convert energy into mechanical energy to drive various types of production machinery, transportation vehicles and items that need to be moved in life.

- High precision: Servo motor is used as the power source, which is composed of ball screw and synchronous belt to form a transmission mechanism with simple structure and high efficiency. Its repeatability error is 0.01%.
- Energy saving: The energy released during the deceleration phase of the working cycle can be converted into electrical energy for reuse, thereby reducing operating costs, and the connected electrical equipment is only 25% of the electrical equipment required for hydraulic drive.
- Precise control: Accurate control is achieved according to the set parameters. With the support of high-precision sensors, measuring devices, and computer technology, it can greatly exceed the control accuracy that other control methods can achieve.
- Improve the level of environmental protection: due to the reduction of the variety of energy used and its optimized performance, the pollution sources are reduced and the noise is reduced, which provides a better guarantee for the environmental protection work of the factory.
- Noise reduction: its operating noise value is lower than 70 decibels, which is about 2/3 of the noise value of hydraulic drive injection molding machines.
- Cost saving: This machine eliminates the cost and trouble of hydraulic oil, has no hard pipes or soft hoses, does not need to cool hydraulic oil, and greatly reduces the cost of cooling water.
3. Pneumatic transmission
Pneumatic transmission is a fluid transmission that uses compressed gas as the working medium and transmits power or information by the pressure of the gas.
Advantage:
1) Using air as the working medium, the working medium is easier to obtain, and the air after use is discharged into the atmosphere, which is convenient to handle. Compared with hydraulic transmission, it is not necessary to set up a recovered oil tank and pipeline.
2) Because the viscosity of air is very small (about 1/10,000 of the dynamic viscosity of hydraulic oil), its loss is also very small, so it is convenient for centralized air supply and long-distance transportation. External leakage will not pollute the environment as seriously as hydraulic transmission.
3) Compared with hydraulic transmission, pneumatic transmission has quick action, quick response, simple maintenance, clean working medium, and no problems such as medium deterioration.
4) Good adaptability to working environment, especially in flammable, explosive, dusty, strong magnetic, radiation, vibration and other harsh working environments, it is superior to hydraulic, electronic and electrical control.
5) Low cost, automatic overload protection.
Shortcoming:
1) Due to the compressibility of air, the working speed is slightly less stable. But the use of gas-liquid linkage device will get more satisfactory results.
2) Due to the low working pressure (generally 0.31MPa) and the size of the structure should not be too large, the total output force should not be greater than 10 ~ 40kN.
3) The noise is large, and a muffler should be added when exhausting at a high speed.
4) The transmission speed of the air signal in the pneumatic device is slower than that of the electron and the speed of light within the speed of sound. Therefore, the pneumatic control system should not be used in a complex circuit with too many components.
4. Hydraulic transmission
Hydraulic transmission is a transmission method that uses liquid as a working medium to transmit energy and control.

Advantage:
1) From the structural point of view, the output power per unit weight and the output power per unit size are overwhelming among the four types of transmission modes, and have a large moment-to-inertia ratio. Small size, light weight, small inertia, compact structure and flexible layout.
2) From the point of view of working performance, speed, torque and power can be adjusted steplessly, the action response is fast, the direction and speed can be changed quickly, the speed regulation range is wide, and the speed regulation range can reach 100:1 to 2000:1; action It has good rapidity, simple control and adjustment, convenient operation and labor saving, easy to cooperate with electrical control and connection with CPU (computer), and easy to realize automation.
3) From the point of view of use and maintenance, the self-lubrication of the components is good, and it is easy to realize overload protection and pressure keeping, which is safe and reliable; the components are easy to realize serialization, standardization and generalization.
4) All equipment using hydraulic technology is safe and reliable.
5) Economy: The plasticity and variability of hydraulic technology are very strong, which can increase the flexibility of flexible production, and it is easy to change and adjust the production process. The manufacturing cost of hydraulic components is relatively low, and the adaptability is relatively strong.
6) The combination of hydraulics and new technologies such as microcomputer control to form “mechanical-electrical-hydraulic-optical” integration has become the trend of world development, which is convenient for digitalization.
Everything is divided into two, there are advantages and disadvantages, hydraulic transmission is no exception:
Shortcoming:
1) The hydraulic transmission inevitably leaks due to the relatively moving surface, and the oil is not absolutely incompressible. In addition to the elastic deformation of the oil pipe, the hydraulic transmission cannot obtain a strict transmission ratio, so it cannot be used for machine tools such as threaded gears. in the inline drive chain.
2) There are edge loss, local loss and leakage loss in the process of oil flow, the transmission efficiency is low, and it is not suitable for long-distance transmission.
3) Under the conditions of high temperature and low temperature, it is difficult to use hydraulic transmission.
4) In order to prevent oil leakage and meet certain performance requirements, the manufacturing precision of hydraulic components is required to be high, which brings certain difficulties to use and maintenance.
5) It is not easy to check when the fault occurs, especially in units with less popular hydraulic technology. This contradiction often hinders the further promotion and application of hydraulic technology. Hydraulic equipment maintenance requires a certain degree of experience, and it takes a long time to train hydraulic technicians.